using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Web.Routing; namespace Swift.MVC { public interface IController { void Execute(RequestContext requestContext); } }
控制器抽象Base类的实现:(这个抽象类的作用更多在于定义一些约束、检查之类)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Swift.MVC { ControllerBase:IController { Execute(System.Web.Routing.RequestContext requestContext); } }
控制器抽象子类的实现:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Swift.MVC { Controller:ControllerBase,IDisposable { Execute(System.Web.Routing.RequestContext requestContext) { //反射得到Action方法 Type type = this.GetType(); ); System.Reflection.MethodInfo mi = type.GetMethod(actionName); //执行该Action方法 mi.Invoke( } public void Dispose() { //throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
这里让Controller类实现IDispose接口,照应了上文控制器工厂里面的ReleaseController()方法,主要起到释放资源的作用。
3、测试及代码释疑由于上述代码用到了System.Web.Routing里面的组件,所以,需要在测试项目里面配置路由规则,这里需要注意一点,我们上面的MvcRouteHandler就是在这里注入进去的。在测试项目里面新建一个全局配置文件如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Routing; using System.Web.Security; using System.Web.SessionState; namespace MyTestMVC { public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication { protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { RouteTable.Routes.Add(, , , action = , id = , assembly = }), new Swift.MVC.MvcRouteHandler())); } protected void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { } } }
然后在测试项目里面模拟MVC新建一个Controllers文件夹,里面新建一个测试的控制器HomeController:
using Swift.MVC; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; namespace MyTestMVC.Controllers { public class HomeController : Controller { public void Index() { HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(); } } }
然后启动项目,访问:16792/Home/Index。运行过程以及代码释疑如下:
(1)来看看 RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context); 这一句
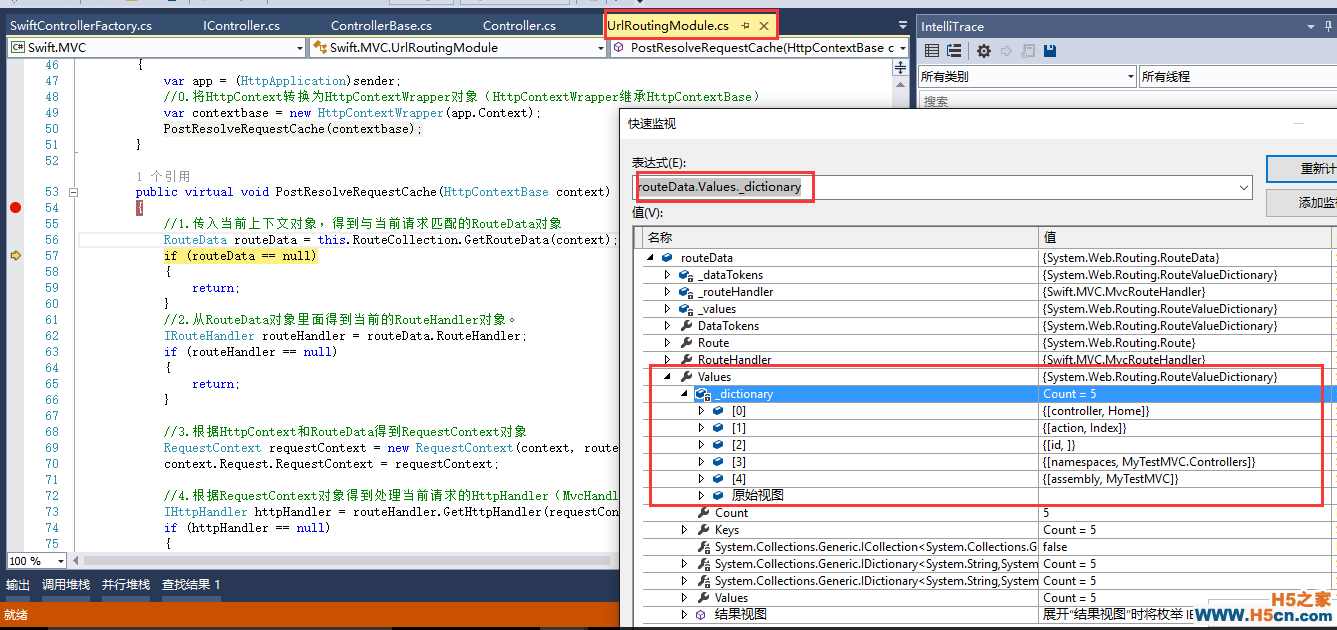
通过上图可知,this.RouteCollection里面保存的是上述全局配置文件里面添加进去的路由规则,然后调用GetRouteData(context)方法,传入当前请求的上下文,得到当前请求的RouteData对象,我们可以看到在这个RouteData对象里面,已经包含了当前请求的控制器和action的名称。
(2)监视 IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler;
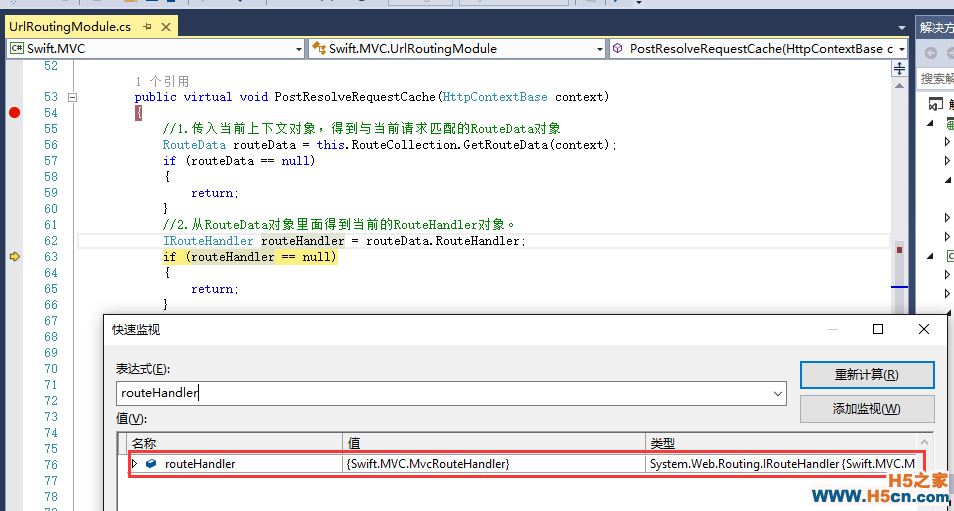
通过上图可以看到在routeData里面我们的RouteHandler已经是MvcRouteHandler对象了,还记得我们在全局配置文件里面有这样一个配置:
RouteTable.Routes.Add(, , , action = , id = , assembly = }), new Swift.MVC.MvcRouteHandler()));
 相关文章
相关文章

 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
