为了使 RapidJSON 简单及快速,我们选择了对赋值采用 * 转移 * 语义。这方法与 std::auto_ptr 相似,都是在赋值时转移拥有权。转移快得多简单得多,只需要析构原来的 Value,把来源 memcpy() 至目标,最后把来源设置为 Null 类型。
因此,使用转移语义后,上面的例子变成:
o();
{
contacts();
// adding elements to contacts array.
o.AddMember("contacts", contacts, d.GetAllocator()); // 只需 memcpy() contacts 本身至新成员的 Value(16 字节)
// contacts 在这里变成 Null。它的析构是平凡的。
}
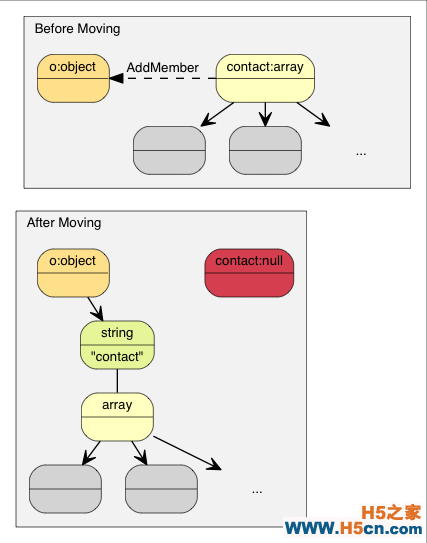
转移语义不需复制。
在 C++11 中这称为转移赋值操作(move assignment operator)。由于 RapidJSON 支持 C++03,它在赋值操作采用转移语义,其它修改形函数如 AddMember(), PushBack() 也采用转移语义。
转移语义及临时值有时候,我们想直接构造一个 Value 并传递给一个“转移”函数(如 PushBack()、AddMember())。由于临时对象是不能转换为正常的 Value 引用,我们加入了一个方便的 Move() 函数:
a();
Document::AllocatorType& allocator = document.GetAllocator();
// a.PushBack(Value(42), allocator); // 不能通过编译
a.PushBack(().SetInt(42), allocator); // fluent API
a.PushBack((42).Move(), allocator); // 和上一行相同
创建 StringRapidJSON 提供两个 String 的存储策略。
Copy-string 总是安全的,因为它拥有数据的克隆。Const-string 可用于存储字符串字面量,以及用于在 DOM 一节中将会提到的 in-situ 解析中。
为了让用户自定义内存分配方式,当一个操作可能需要内存分配时,RapidJSON 要求用户传递一个 allocator 实例作为 API 参数。此设计避免了在每个 Value 存储 allocator(或 document)的指针。
因此,当我们把一个 copy-string 赋值时, 调用含有 allocator 的 SetString() 重载函数:
document;
author;
char buffer[10];
int len = sprintf(buffer, "%s %s", "Milo", "Yip"); // 动态创建的字符串。
author.SetString(buffer, len, document.GetAllocator());
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
// 清空 buffer 后 author.GetString() 仍然包含 "Milo Yip"
在此例子中,我们使用 Document 实例的 allocator。这是使用 RapidJSON 时常用的惯用法。但你也可以用其他 allocator 实例。
另外,上面的 SetString() 需要长度参数。这个 API 能处理含有空字符的字符串。另一个 SetString() 重载函数没有长度参数,它假设输入是空字符结尾的,并会调用类似 strlen() 的函数去获取长度。
最后,对于字符串字面量或有安全生命周期的字符串,可以使用 const-string 版本的 SetString(),它没有 allocator 参数。对于字符串家面量(或字符数组常量),只需简单地传递字面量,又安全又高效:
s;
s.SetString("rapidjson"); // 可包含空字符,长度在编译萁推导
s = "rapidjson"; // 上行的缩写
对于字符指针,RapidJSON 需要作一个标记,代表它不复制也是安全的。可以使用 StringRef 函数:
const char * cstr = getenv("USER");
size_t cstr_len = ...; // 如果有长度
s;
// s.SetString(cstr); // 这不能通过编译
s.SetString((cstr)); // 可以,假设它的生命周期安全,并且是以空字符结尾的
s = (cstr); // 上行的缩写
s.SetString((cstr, cstr_len));// 更快,可处理空字符
s = (cstr, cstr_len); // 上行的缩写
修改 ArrayArray 类型的 Value 提供与 std::vector 相似的 API。
注意,Reserve(...) 及 PushBack(...) 可能会为数组元素分配内存,所以需要一个 allocator。
以下是 PushBack() 的例子:
a();
Document::AllocatorType& allocator = document.GetAllocator();
for (int i = 5; i <= 10; i++)
a.PushBack(i, allocator); // 可能需要调用 realloc() 所以需要 allocator
// 流畅接口(Fluent interface)
a.PushBack("Lua", allocator).PushBack("Mio", allocator);
与 STL 不一样的是,PushBack()/PopBack() 返回 Array 本身的引用。这称为流畅接口(_fluent interface_)。
如果你想在 Array 中加入一个非常量字符串,或是一个没有足够生命周期的字符串(见 ),你需要使用 copy-string API 去创建一个 String。为了避免加入中间变量,可以就地使用一个 :
// 就地 Value 参数
contact.PushBack(("copy", document.GetAllocator()).Move(), // copy string
document.GetAllocator());
// 显式 Value 参数
val("key", document.GetAllocator()); // copy string
contact.PushBack(val, document.GetAllocator());
修改 ObjectObject 是键值对的集合。每个键必须为 String。要修改 Object,方法是增加或移除成员。以下的 API 用来增加城员:
以下是一个例子。
contact(kObject);
contact.AddMember("name", "Milo", document.GetAllocator());
contact.AddMember("married", true, document.GetAllocator());
使用 StringRefType 作为 name 参数的重载版本与字符串的 SetString 的接口相似。 这些重载是为了避免复制 name 字符串,因为 JSON object 中经常会使用常数键名。
如果你需要从非常数字符串或生命周期不足的字符串创建键名(见 ),你需要使用 copy-string API。为了避免中间变量,可以就地使用 :
// 就地 Value 参数
contact.AddMember(("copy", document.GetAllocator()).Move(), // copy string
().Move(), // null value
document.GetAllocator());
// 显式参数
key("key", document.GetAllocator()); // copy string name
val(42); // 某 Value
contact.AddMember(key, val, document.GetAllocator());
移除成员有几个选择:
MemberIterator RemoveMember(MemberIterator) 使用了“转移最后”手法来达成常数时间复杂度。基本上就是析构迭代器位置的成员,然后把最后的成员转移至迭代器位置。因此,成员的次序会被改变。
深复制 Value若我们真的要复制一个 DOM 树,我们可使用两个 APIs 作深复制:含 allocator 的构造函数及 CopyFrom()。
d;
Document::AllocatorType& a = d.GetAllocator();
v1("foo");
// Value v2(v1); // 不容许
v2(v1, a); // 制造一个克隆
assert(v1.IsString()); // v1 不变
d.SetArray().PushBack(v1, a).PushBack(v2, a);
assert(v1.IsNull() && v2.IsNull()); // 两个都转移动 d
v2.CopyFrom(d, a); // 把整个 document 复制至 v2
assert(d.IsArray() && d.Size() == 2); // d 不变
v1.SetObject().AddMember("array", v2, a);
d.PushBack(v1, a);
交换 ValueRapidJSON 也提供 Swap()。
a(123);
b("Hello");
a.Swap(b);
assert(a.IsString());
assert(b.IsInt());
无论两棵 DOM 树有多复杂,交换是很快的(常数时间)。
下一部分本教程展示了如何询查及修改 DOM 树。RapidJSON 还有一个重要概念:
你也可以参考 常见问题、API 文档、例子及单元测试。
 相关文章
相关文章


![JsBin[使用教程]](/upload8/allimg/161017/13023G619_lit.png)
 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
