本教程简介文件对象模型(Document Object Model, DOM)API。
如 中所示,可以解析一个 JSON 至 DOM,然后就可以轻松查询及修改 DOM,并最终转换回 JSON。
Value 及 Document每个 JSON 值都储存为 Value 类,而 Document 类则表示整个 DOM,它存储了一个 DOM 树的根 Value。RapidJSON 的所有公开类型及函数都在 rapidjson 命名空间中。
查询 Value在本节中,我们会使用到 example/tutorial/tutorial.cpp 中的代码片段。
假设我们用 C 语言的字符串储存一个 JSON(const char* json):
{
"hello": "world",
"t": true ,
"f": false,
"n": null,
"i": 123,
"pi": 3.1416,
"a": [1, 2, 3, 4]
}
把它解析至一个 Document:
#include "rapidjson/document.h"
using namespace rapidjson;
// ...
Document document;
document.(json);
那么现在该 JSON 就会被解析至 document 中,成为一棵 *DOM 树 *:
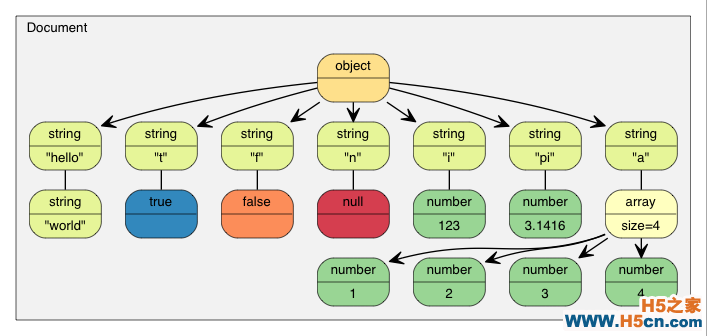
教程中的 DOM
自从 RFC 7159 作出更新,合法 JSON 文件的根可以是任何类型的 JSON 值。而在较早的 RFC 4627 中,根值只允许是 Object 或 Array。而在上述例子中,根是一个 Object。
assert(document.IsObject());
让我们查询一下根 Object 中有没有 "hello" 成员。由于一个 Value 可包含不同类型的值,我们可能需要验证它的类型,并使用合适的 API 去获取其值。在此例中,"hello" 成员关联到一个 JSON String。
assert(document.HasMember("hello"));
assert(document["hello"].IsString());
printf("hello = %s\n", document["hello"].GetString());
world
JSON True/False 值是以 bool 表示的。
assert(document["t"].IsBool());
printf("t = %s\n", document["t"].GetBool() ? "true" : "false");
true
JSON Null 值可用 IsNull() 查询。
printf("n = %s\n", document["n"].IsNull() ? "null" : "?");
null
JSON Number 类型表示所有数值。然而,C++ 需要使用更专门的类型。
assert(document["i"].IsNumber());
// 在此情况下,IsUint()/IsInt64()/IsUInt64() 也会返回 true
assert(document["i"].IsInt());
printf("i = %d\n", document["i"].GetInt());
// 另一种用法: (int)document["i"]
assert(document["pi"].IsNumber());
assert(document["pi"].IsDouble());
printf("pi = %g\n", document["pi"].GetDouble());
i = 123
pi = 3.1416
JSON Array 包含一些元素。
// 使用引用来连续访问,方便之余还更高效。
const & a = document["a"];
assert(a.IsArray());
for ( i = 0; i < a.Size(); i++) // 使用 SizeType 而不是 size_t
printf("a[%d] = %d\n", i, a[i].GetInt());
a[0] = 1
a[1] = 2
a[2] = 3
a[3] = 4
注意,RapidJSON 并不自动转换各种 JSON 类型。例如,对一个 String 的 Value 调用 GetInt() 是非法的。在调试模式下,它会被断言失败。在发布模式下,其行为是未定义的。
以下将会讨论有关查询各类型的细节。
查询 Array缺省情况下,SizeType 是 unsigned 的 typedef。在多数系统中,Array 最多能存储 2^32-1 个元素。
你可以用整数字面量访问元素,如 a[0]、a[1]、a[2]。
Array 与 std::vector 相似,除了使用索引,也可使用迭代器来访问所有元素。
for (Value::ConstValueIterator itr = a.Begin(); itr != a.End(); ++itr)
printf("%d ", itr->GetInt());
还有一些熟悉的查询函数:
当使用 C++11 功能时,你可使用范围 for 循环去访问 Array 内的所有元素。
for (auto& v : a.GetArray())
printf("%d ", v.GetInt());
查询 Object和 Array 相似,我们可以用迭代器去访问所有 Object 成员:
* kTypeNames[] =
{ "Null", "False", "True", "Object", "Array", "String", "Number" };
for (Value::ConstMemberIterator itr = document.MemberBegin();
itr != document.MemberEnd(); ++itr)
{
printf("Type of member %s is %s\n",
itr->name.GetString(), kTypeNames[itr->value.GetType()]);
}
of member hello is String
of member t is True
of member f is False
of member n is Null
of member i is Number
of member pi is Number
of member a is Array
注意,当 operator[](const char*) 找不到成员,它会断言失败。
若我们不确定一个成员是否存在,便需要在调用 operator[](const char*) 前先调用 HasMember()。然而,这会导致两次查找。更好的做法是调用 FindMember(),它能同时检查成员是否存在并返回它的 Value:
Value::ConstMemberIterator itr = document.FindMember("hello");
if (itr != document.MemberEnd())
printf("%s\n", itr->value.GetString());
范围 for 循环 (v1.1.0 中的新功能)当使用 C++11 功能时,你可使用范围 for 循环去访问 Object 内的所有成员。
for (auto& m : document.GetObject())
printf("Type of member %s is %s\n",
m.name.GetString(), kTypeNames[m.value.GetType()]);
查询 NumberJSON 只提供一种数值类型──Number。数字可以是整数或实数。RFC 4627 规定数字的范围由解析器指定。
由于 C++ 提供多种整数及浮点数类型,DOM 尝试尽量提供最广的范围及良好性能。
当解析一个 Number 时, 它会被存储在 DOM 之中,成为下列其中一个类型:
类型 描述
unsigned 32 位无号整数
int 32 位有号整数
uint64_t 64 位无号整数
int64_t 64 位有号整数
double 64 位双精度浮点数
当查询一个 Number 时, 你可以检查该数字是否能以目标类型来提取:
查检 提取
bool IsNumber() 不适用
bool IsUint() unsigned GetUint()
bool IsInt() int GetInt()
bool IsUint64() uint64_t GetUint64()
bool IsInt64() int64_t GetInt64()
bool IsDouble() double GetDouble()
 相关文章
相关文章


![JsBin[使用教程]](/upload8/allimg/161017/13023G619_lit.png)
 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
