本文翻译来自:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/what-is-new/index
一.模型级查询过滤器(Model-level query filters)ef core2.0包含了一个新特性,我们叫他模型级查询过滤器(Model-level query filters)。此特性允许使用Linq查询表达式直接定义在实体类型的元数据模型上。这样的过滤器会自动应用到任何LINQ查询所涉及的那些实体类型,包括间接引用的实体类型(对象引用,导航属性)。这个特性的一些常见应用是:
示例代码:
BloggingContext : DbContext 2 { 3 public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; } 4 public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; } TenantId {get; set; } OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) 9 { 10 modelBuilder.Entity<Post>().HasQueryFilter( 11 p => !p.IsDeleted 12 && p.TenantId == this.TenantId ); 13 } 14 }
我们给 Post 实体类型定义了一个模型级查询过滤器,实现了多租户和软删除。模型级过滤器将使用正确的上下文实例中的值,即执行查询的那个。
使用 IgnoreQueryFilters() 方法在一次查询中禁用过滤器。
局限性:
这是两种可选择的性能特性之一,旨在在高并发场景中提供更好的性能支持。
在 ef core 2.0 中,我们将自定义的DbContext类型注册到DbContextPool服务中,可让该数据库上下文类型的实例重复使用。
示例代码:
services.AddDbContextPool<BloggingContext>( options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
如果使用这种方法,当一个控制器请求一个DbContext的实例时,首先会检查是否在DbContextPool存在该类型的实例,当一次请求结束后,任何状态的DbContext实例都会被重置,且将自身加入到DbContextPool中。
这在概念上类似于ADO.NET提供的数据库连接池,旨在节省一些DbContext实例初始化的成本。
三.显式编译查询(Explicitly compiled queries)
这是两种可选择的性能特性之二 。
在以前的ef版本中,调用查询api时,可以通过自动编译并缓存编译的结果达到一次计算多次调用,有效的提高了ef的性能,显示编译查询(Explicitly compiled queries)这种机制可以绕过缓存查找的性能消耗,直接调用已经编译好的表达式,获得一个小的性能提升。
示例代码:
Func<CustomerContext, int, Customer> _customerById = 3 EF.CompileQuery((CustomerContext db, int id) => 4 db.Customers 5 .Include(c => c.Address) 6 .Single(c => c.Id == id)); (var db = new CustomerContext()) 10 { 11 var customer = _customerById(db, 147); 12 }
四.在使用FromSql和ExecuteSqlCommand方法时加入参数化查询
在使用C#6.0的特性构建SQL语句并使用FromSql和ExecuteSqlCommand方法执行SQL语句时,会自动加入使用参数化查询,防止SQL注入。
示例代码:
; ; (var context = CreateContext()) 5 { 6 context.Set<Customer>() 7 .FromSql($@" 8 SELECT * 9 FROM ""Customers"" 10 WHERE ""City"" = {city} AND ) 12 .ToArray(); 13 }
上面的代码生成的SQL:
@p0=(Size = 4000) @p1=(Size = 4000) SELECT * FROM ""Customers"" WHERE ""City"" = @p0 AND ""ContactTitle"" = @p1
五.Attach can track a graph of new and existing entities
EF Core supports automatic generation of key values through a variety of mechanisms. When using this feature, a value is generated if the key property is the CLR default--usually zero or null. This means that a graph of entities can be passed to DbContext.Attach or DbSet.Attach and EF Core will mark those entities that have a key already set as Unchanged while those entities that do not have a key set will be marked as Added . This makes it easy to attach a graph of mixed new and existing entities when using generated keys. DbContext.Update and DbSet.Update work in the same way, except that entities with a key set are marked as Modified instead of Unchanged .
六.表拆分(Table splitting)
现在可以将两个或多个实体类型映射到同一表,其中主键列将被共享,每一行对应两个或多个实体。
要使用表拆分,必须在共享表的所有实体类型之间配置标识关系(外键属性构成主键)
示例代码:
 相关文章
相关文章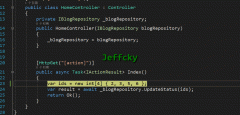


 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
