在人工智能进展的如火如荼的今天,我们如果不尝试去接触新鲜事物,马上就要被世界淘汰啦~
本文拟使用Python开发语言实现类似于WIndows平台的“小娜”,或者是IOS下的“Siri”。最终达到人机对话的效果。
【实现功能】这篇文章将要介绍的主要内容如下:
1、搭建人工智能--人机对话服务端平台 2、实现调用服务端平台进行人机对话交互 【实现思路】AIML
AIML由Richard Wallace发明。他设计了一个名为 A.L.I.C.E. (Artificial Linguistics Internet Computer Entity 人工语言网计算机实体) 的机器人,并获得了多项人工智能大奖。有趣的是,图灵测试的其中一项就在寻找这样的人工智能:人与机器人通过文本界面展开数分钟的交流,以此查看机器人是否会被当作人类。
本文就使用了Python语言调用AIML库进行智能机器人的开发。
本系统的运作方式是使用Python搭建服务端后台接口,供各平台可以直接调用。然后客户端进行对智能对话api接口的调用,服务端分析参数数据,进行语句的分析,最终返回应答结果。
当前系统前端使用HTML进行简单地聊天室的设计与编写,使用异步请求的方式渲染数据。
【开发及部署环境】开发环境:Windows 7 ×64 英文版
JetBrains PyCharm 2017.1.3 x64
测试环境:Windows 7 ×64 英文版
【所需技术】 1、Python语言的熟练掌握,Python版本2.7 2、Python服务端开发框架tornado的使用 3、aiml库接口的简单使用 4、HTML+CSS+Javascript(jquery)的熟练使用 5、Ajax技术的掌握 【实现过程】 1、安装Python aiml库pip install aiml
2、获取alice资源 Python aiml安装完成后在Python安装目录下的 Lib/site-packages/aiml下会有alice子目录,将此目录复制到工作区。
或者在Google code上下载alice brain: aiml-en-us-foundation-alice.v1-9.zip
取得alice资源之后就可以直接利用Python aiml库加载alice brain了:
import aiml os.chdir() # 将工作区目录切换到刚才复制的alice文件夹 alice = aiml.Kernel() alice.learn() alice.respond()
注意加载时需要切换工作目录到alice(刚才复制的文件夹)下。
4、 与alice聊天加载之后就可以与alice聊天了,每次只需要调用respond接口:
alice.respond() #这里的hello即为发给机器人的信息
5. 用Tornado搭建聊天机器人网站Tornado可以很方便地搭建一个web网站的服务端,并且接口风格是Rest风格,可以很方便搭建一个通用的服务端接口。
这里写两个方法:
get:渲染界面
post:获取请求参数,并分析,返回聊天结果
Class类的代码如下:
class ChatHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.render() def post(self): try: message = self.get_argument(, None) print(str(message)) result = { : True, : str(alice.respond(message)) } print(str(result)) respon_json = tornado.escape.json_encode(result) self.write(respon_json) except Exception, ex: repr(ex) print(str(ex)) result = { : False, : '' } self.write(str(result))
6. 简单搭建一个聊天界面
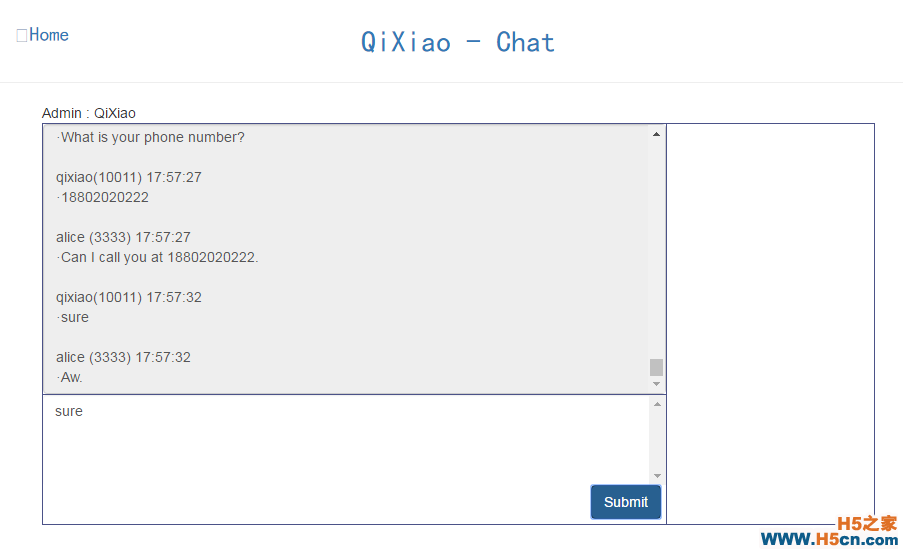
该界面是基于BootStrap的,我们简单搭建这么一个聊天的界面用于展示我们的接口结果。同时进行简单的聊天。
6. 接口调用我们异步请求服务端接口,并将结果渲染到界面
$.ajax({ type: 'post', url: AppDomain+'chat', async: true,//异步 dataType: 'json', data: ( { "msg":request_txt }), success: function (data) { console.log(JSON.stringify(data)); if (data.is_success == true) { setView(resUser,data.message); } }, error: function (data) { console.log(JSON.stringify(data)); } });//end Ajax
这里我附上系统的完整目录结构以及完整代码->
7、目录结构

os.path import tornado.auth import tornado.escape import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornado.options import tornado.web from tornado.options import define, options import os import aiml os.chdir() alice = aiml.Kernel() alice.learn() alice.respond() define(, default=3999, help=, type=int) class Application(tornado.web.Application): def __init__(self): handlers = [ (r, MainHandler), (r, ChatHandler), ] settings = dict( template_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(), static_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(), debug=True, ) tornado.web.Application.__init__(self, handlers, **settings) class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.render() def post(self): result = { : True, : } respon_json = tornado.escape.json_encode(result) self.write(str(respon_json)) def put(self): respon_json = tornado.escape.json_encode() self.write(respon_json) class ChatHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler): def get(self): self.render() def post(self): try: message = self.get_argument(, None) print(str(message)) result = { : True, : str(alice.respond(message)) } print(str(result)) respon_json = tornado.escape.json_encode(result) self.write(respon_json) except Exception, ex: repr(ex) print(str(ex)) result = { : False, : '' } self.write(str(result)) def main(): tornado.options.parse_command_line() http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(Application()) http_server.listen(options.port) tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() : ) main()
View Code 9、Html前端代码
 相关文章
相关文章

 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
