ASP.NET页面运行时候,页面将经历一个生命周期,在生命周期中将执行一系列的处理步骤。包括初始化、实例化控件、还原和维护状态、运行时间处理程序代码以及进行呈现。熟悉页面生命周期非常重要,这样我们才能在生命周期的合适阶段编写代码。如果我们能在写代码的时候想着我们现在是在做生命周期的哪一步那将是非常好的。
你可能会说我不清楚还不是一样写代码,反正每次都在Page_load里面写代码 然后页面就出来了我管那么多干什么。所谓知其然如果能知其所以然岂不是更吊?我个人认为做ASP.NET B/S开发只要咱们熟悉ASP.NET页面生命周期,熟悉“请求-处理-响应“模式,对于一时半儿没有触及到的细节,等真正遇到那个点再去理解它也是毫不费力的。
几个代表性的问题在开始的时候我们先思考几个问题,看看我们在描述完页面生命周期的时候,能不能回答上这几个问题
1.为什么在服务器端能通过this.textbox1.Text获取到用户提交过来的数据?
2.在Page_Load中Response.Write("hello")查看生成的html代码原文件,hello在哪里?为什么?
3.有一个服务器端的按钮,设置了点击事件,该点击事件什么时候执行?是先执行Page_Load事件还是先执行点击事件?
4.为什么在服务器端通过this.textbox1.Text设置值后,客户端就能显示出来?
下面主要讲述的就是ASP.NET WebForm中的页面的生命周期了。
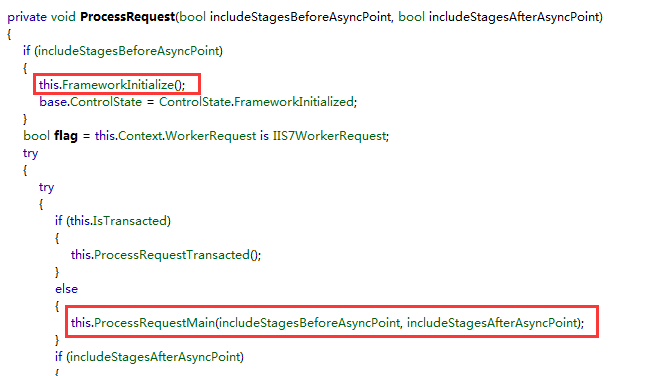
我们用反编译工具查看Page类的ProcessRequest方法可以看见先调用了FrameworkInitialize; FrameworkInitialize里面就是打造了页面控件树,然后调用了ProcessRequestMain,就开始了执行整个页面生命周期了(其实就是调用了一系列的事件方法)(可能部分图看不见右边,可在新标签页中打开图片)
1.打造页面控件树 FrameworkInitialize内部调用了_buildControlTree()方法
上图中左边是前台页面的代码,右边是对应 生成的打造控件树的代码。中间截取的是生成表单那一部分的代码。 下面看一张原理图

2.触发PerformPreInit事件
在所有初始化之前初始化了这个事件,这个事件主要是初始化了主题,初始化了母版页
PerformPreInit() 2 3 { .OnPreInit(EventArgs.Empty); .InitializeThemes(); .ApplyMasterPage(); ._preInitWorkComplete = true; 12 13 }
View Code
3.触发InitRecursive事件

4.触发LoadAllState()事件
5.触发ProcessPostData(this._requestValueCollection, true)事件
ProcessPostData(NameValueCollection postData, bool fBeforeLoad) 2 { 3 if (this._changedPostDataConsumers == null) 4 { 5 this._changedPostDataConsumers = new ArrayList(); 6 } 7 if (postData != null) 8 { 9 foreach (string str in postData) 10 { 11 if ((str != null) && !IsSystemPostField(str)) 12 { 13 Control control = this.FindControl(str); 14 if (control == null) 15 { 16 if (fBeforeLoad) 17 { 18 if (this._leftoverPostData == null) 19 { 20 this._leftoverPostData = new NameValueCollection(); 21 } 22 this._leftoverPostData.Add(str, null); 23 } 24 } { 27 IPostBackDataHandler postBackDataHandler = control.PostBackDataHandler; 28 if (postBackDataHandler == null) 29 { 30 if (control.PostBackEventHandler != null) 31 { 32 this.RegisterRequiresRaiseEvent(control.PostBackEventHandler); 33 } 34 } { 37 if (postBackDataHandler != null) 38 { 39 NameValueCollection postCollection = control.CalculateEffectiveValidateRequest() ? this._requestValueCollection : this._unvalidatedRequestValueCollection; 40 if (postBackDataHandler.LoadPostData(str, postCollection)) 41 { 42 this._changedPostDataConsumers.Add(control); 43 } 44 } 45 if (this._controlsRequiringPostBack != null) 46 { 47 this._controlsRequiringPostBack.Remove(str); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 ArrayList list = null; 55 if (this._controlsRequiringPostBack != null) 56 { ._controlsRequiringPostBack) 58 { 59 Control control2 = this.FindControl(str2); 60 if (control2 != null) 61 { 62 IPostBackDataHandler adapterInternal = control2.AdapterInternal as IPostBackDataHandler; 63 if (adapterInternal == null) 64 { 65 adapterInternal = control2 as IPostBackDataHandler; 66 } 67 if (adapterInternal == null) 68 { [] { str2 }; HttpException(SR.GetString(, args)); 71 } 72 NameValueCollection values2 = control2.CalculateEffectiveValidateRequest() ? this._requestValueCollection : this._unvalidatedRequestValueCollection; 73 if (adapterInternal.LoadPostData(str2, values2)) 74 { 75 this._changedPostDataConsumers.Add(control2); 76 } 77 } (fBeforeLoad) 79 { 80 if (list == null) 81 { 82 list = new ArrayList(); 83 } 84 list.Add(str2); 85 } 86 } 87 this._controlsRequiringPostBack = list; 88 } 89 }
View Code
 相关文章
相关文章


 精彩导读
精彩导读 热门资讯
热门资讯 关注我们
关注我们
